|





To select an engine-driven generator, you’ll need to determine the power (kilowatt) requirements which
must be met under operating conditions. Undersizing the generator can be avoided by considering all of the loads that will
be connected to the generator, and by determining the starting requirements (motor start) of electric motor-operated devices.
Be sure the generator you select is large enough to handle your present requirements and anticipated needs.
To determine the right size generator, add up the total watts of all lights, appliances, tools, or other equipment to be connected to the generator. Check the nameplates to determine wattage.
If wattage is not shown, but amps and volts are given, the following simplified formula may be used:
Amps x Volts = Watts
(Ex. 12.5 amps x 120 volts = 1,500 watts)
To determine kilowatts (kW), use the following formula:
1,000 Watts = 1 Kilowatt
(Ex. 1,500 Watts/1,000 = 1.5 kW)
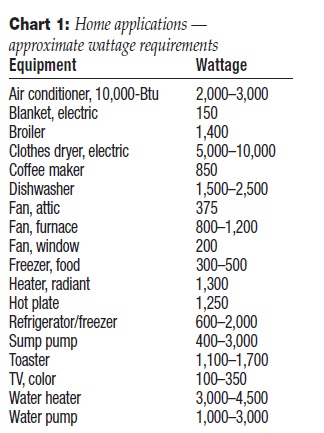
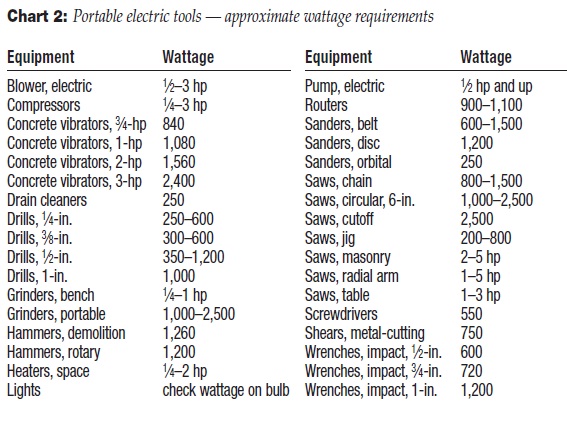
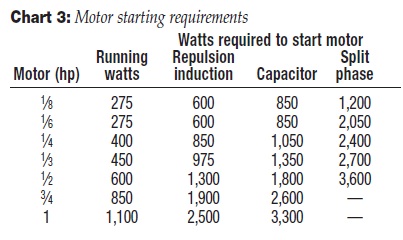
Charts 1, 2, and 3 shown will
help you in selecting the proper size generator. With lights,
heaters, and small appliances, simply add the nameplate ratings or see Chart 1 for average wattage requirements. For portable
electric tools and equipment, check the nameplate rating or use Chart 2 for average requirements. If watts and/or amps are
not given and only the horsepower is shown, use Chart 3 to determine the starting and running watts.
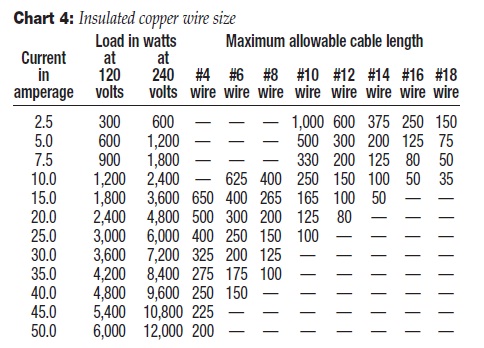
Chart 4 is furnished as a guide
for selecting the proper size of insulated copper wire when extension cables are used. We recommend the use of outdoor-rated
(U.L.) cable, recognized type SJTW-A.
|

